Wireless garage door remotes have become an essential convenience for homeowners, allowing for the seamless and secure operation of garage doors. Given the variety of garage door opener models available, manufacturers of these remotes face the critical task of ensuring compatibility across different systems. Here’s an exploration of the strategies and technologies they employ to achieve this compatibility.
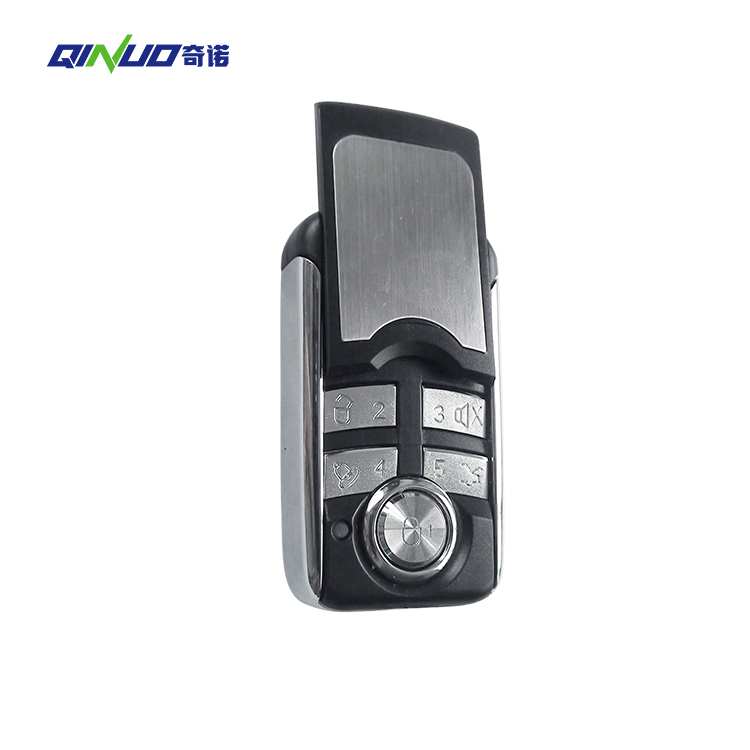

1. Universal Remote Designs
One of the most effective approaches is the development of universal remotes. These devices are designed to work with a wide range of garage door opener brands and models. Manufacturers achieve this universality through several means:
Multiple Frequency Support: Garage door openers operate on various frequencies, typically in the range of 300 MHz to 390 MHz. Universal remotes are built to support multiple frequencies, allowing them to communicate with openers regardless of their specific operating frequency.
Programmable Codes: Universal remotes often come with programmable features that enable them to learn the specific code sequences used by different garage door openers. This is typically achieved through a simple setup process where the remote captures and stores the code transmitted by the original remote or the opener unit.
2. Database of Compatible Models
Manufacturers maintain extensive databases of garage door opener models and their corresponding operating specifications. By regularly updating these databases, they ensure that their remotes remain compatible with the latest models on the market. This database approach allows manufacturers to pre-program their remotes with the necessary codes and frequencies for a wide array of garage door openers.
3. Learning Capabilities
Many modern garage door remotes are equipped with learning capabilities. This feature allows the remote to automatically detect and adapt to the code and frequency used by a particular garage door opener. The learning process typically involves the following steps:
Initiation: The user presses a specific button on the remote to start the learning mode.
Transmission: The garage door opener or its existing remote sends out a signal.
Acquisition: The new remote receives and stores this signal, enabling it to replicate the necessary code and frequency for future operations.
4. Manufacturing Partnerships and Licensing
Manufacturers often establish partnerships with major garage door opener brands. These collaborations can involve licensing agreements that provide remote manufacturers with access to proprietary technologies and specifications. Such partnerships ensure that third-party remotes are designed to be fully compatible with the proprietary systems of leading garage door opener manufacturers.
5. Standardization and Compliance
Adhering to industry standards and compliance requirements is another crucial aspect. Organizations like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States set regulations regarding the operation of wireless devices. By complying with these standards, remote manufacturers ensure their products can legally and effectively operate across different garage door opener systems. Compliance includes adhering to specific frequency bands, power levels, and signal encoding techniques.
6. Consumer-Friendly Design and Instructions
To ensure ease of use and compatibility, manufacturers provide detailed instructions and customer support for the setup and programming of their remotes. These instructions often include:
Step-by-Step Guides: Clear, easy-to-follow steps that help users program their remotes to work with their specific garage door opener models.
Online Resources: Websites, videos, and FAQ sections that offer additional assistance and troubleshooting tips.
Customer Support: Access to customer service representatives who can provide real-time support and guidance.
7. Firmware Updates
Some advanced wireless remotes come with the capability for firmware updates. This allows manufacturers to release updates that users can install to ensure continued compatibility with new garage door opener models or to fix any issues that arise. Firmware updates can be applied via USB connections, wireless downloads, or through dedicated smartphone apps.
Conclusion
Ensuring compatibility between wireless garage door remotes and various garage door opener models involves a multifaceted approach. Manufacturers utilize universal designs, maintain extensive model databases, implement learning capabilities, and establish industry partnerships to achieve broad compatibility. Adherence to regulatory standards and providing robust customer support further enhance the usability and reliability of these remotes. As technology evolves, continuous updates and innovations in remote design will ensure that they remain an indispensable convenience for homeowners worldwide.

-
Office ViewQinuo Electronics Co., Ltd.was founded in 2009,it is a high-tech company that integrated R & D, manufacturing, sales and service for 15 years,which is mainly specialized in providing sensors of automatic door, control system of door and gate, car key remote, auto parts etc. The company currently has four independent brands: U-CONTROL, U-SENSORS, U-AUTOGATES and U-AUTOKEYS.
-
got questions? call us
+86 13960286508
-
fax :
+86 595 22901208 -
Email :
[email protected]
-
address
- No.991 Xingxiu Road,Taiwanese Investment Zone, Quanzhou, Fujian Province,P.R.China