Rolling code garage door remotes represent a significant advancement in the security of garage door systems. Designed to prevent unauthorized access, they employ dynamic codes that change with each use, making it exceedingly difficult for potential hackers to gain entry. This article explores the security features of rolling code technology and evaluates its effectiveness against hacking attempts.
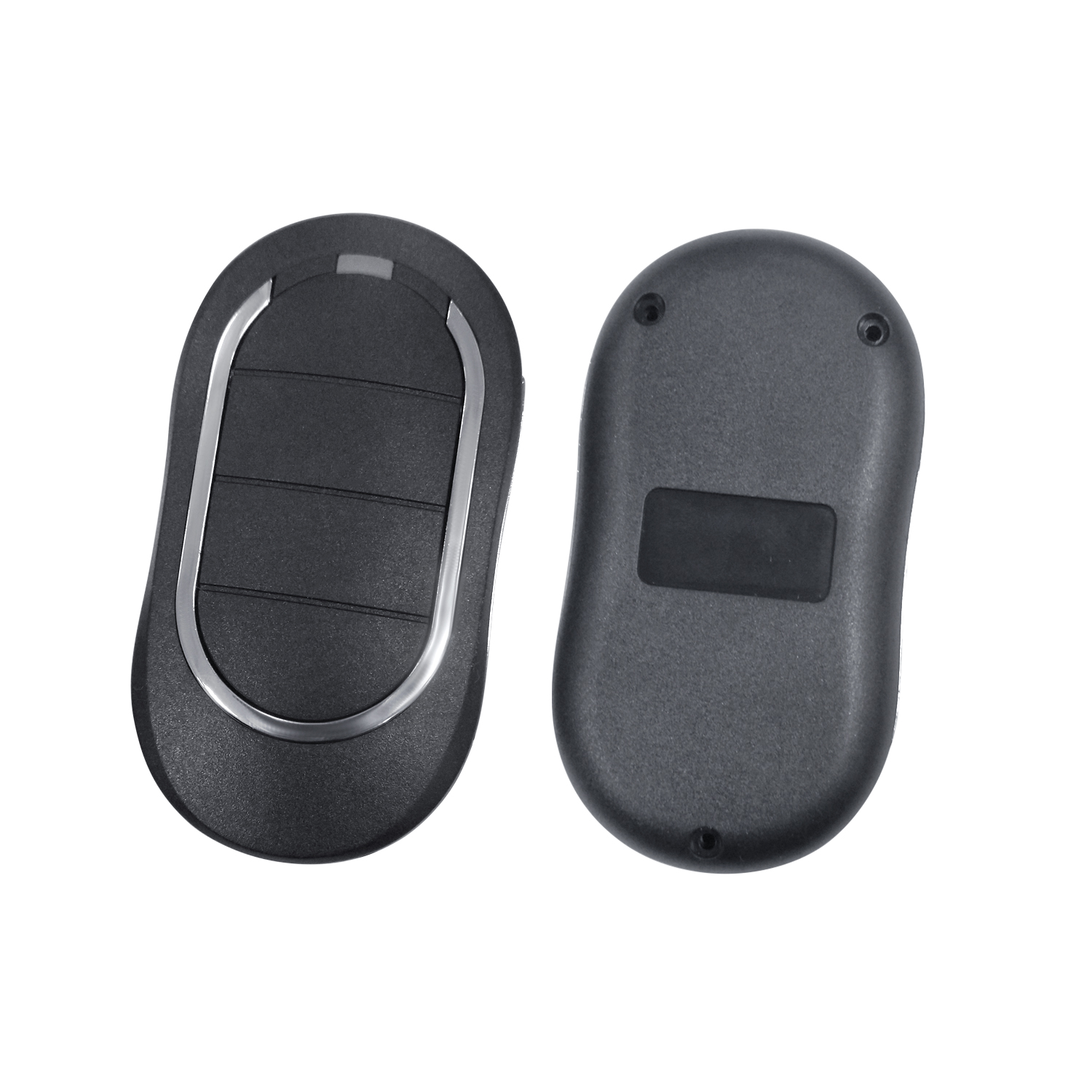

Understanding Rolling Code Technology
Rolling code technology, also known as hopping code, was developed to address the vulnerabilities of fixed code systems. In fixed code systems, the same code is transmitted every time the remote is used, making it relatively easy for hackers to intercept and replicate the signal. Rolling code systems, on the other hand, generate a new code each time the remote button is pressed. Both the remote and the garage door opener use an algorithm to stay in sync, ensuring that the code is only used once and then discarded.
How Rolling Code Technology Enhances Security
1. Dynamic Code Generation:
Each time the remote is activated, a unique code is generated using a complex algorithm. This code is sent to the garage door opener, which recognizes it and allows the door to be opened. The code is then invalidated and cannot be reused.
2. Synchronization Mechanism:
The remote and the opener remain in sync by using a shared algorithm. Even if a code is intercepted, it becomes useless because it cannot be reused and the next valid code is unpredictable.
3. Large Code Space:
Rolling code systems typically use a large code space, often 32-bit or 64-bit, resulting in billions or even trillions of possible codes. This makes it nearly impossible for hackers to guess or brute-force the correct code.
Potential Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures
While rolling code technology significantly enhances security, no system is entirely immune to sophisticated attacks. Understanding potential vulnerabilities can help users and manufacturers improve defenses.
1. Relay Attacks:
Threat: In a relay attack, hackers use two devices to intercept and relay the signal from the remote to the garage door opener, tricking the system into thinking the remote is nearby.
Countermeasures: Proximity-based authentication systems can help mitigate this risk by ensuring that the remote must be physically close to the opener.
2. Replay Attacks:
Threat: Although rolling code systems are designed to prevent replay attacks, sophisticated hackers might attempt to capture and replay signals in rare cases where the system is not perfectly implemented.
Countermeasures: Ensuring that the system properly invalidates used codes and maintaining regular updates to the rolling code algorithm can prevent such attacks.
3. Signal Jamming:
Threat: Hackers can jam the signal between the remote and the opener, preventing the code from being received and causing synchronization issues.
Countermeasures: Advanced systems can detect jamming attempts and employ fallback security measures, such as requiring physical key access during suspicious activity.
4. Physical Security:
Threat: Physical access to the garage door opener or the remote can compromise security, as hackers might manipulate the devices directly.
Countermeasures: Ensuring the physical security of both the remote and the opener, such as storing the remote in a secure location and using tamper-resistant hardware, can mitigate these risks.
Comparative Security Analysis
1. Against Fixed Code Systems:
Rolling code systems are significantly more secure than fixed code systems. Fixed codes can be easily intercepted and reused, while rolling codes provide dynamic security that is much harder to bypass.
2. Against Smart Home Systems:
Some smart home systems also use advanced encryption and authentication methods. Rolling code remotes offer comparable security and can be integrated into smart home setups for enhanced overall protection.
Best Practices for Users
1. Regular Updates:
Ensure your garage door opener’s firmware is regularly updated to protect against new vulnerabilities and hacking techniques.
2. Secure Storage:
Store your remote in a secure location, such as a locked drawer or a specialized key safe, to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Enhanced Security Features:
Consider garage door openers with additional security features like encryption, two-factor authentication, or integration with home security systems.
4. Physical Barriers:
Implement physical security measures, such as robust locks and security cameras, to deter potential hackers and burglars.
Conclusion
Rolling code garage door remotes offer a high level of security against hacking attempts by using dynamic code generation and synchronization mechanisms. While no system is entirely impervious to sophisticated attacks, rolling code technology provides robust protection that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. By understanding potential vulnerabilities and adopting best practices, users can further enhance the security of their rolling code garage door systems and enjoy peace of mind knowing their homes are well protected.

-
Office ViewQinuo Electronics Co., Ltd.was founded in 2009,it is a high-tech company that integrated R & D, manufacturing, sales and service for 15 years,which is mainly specialized in providing sensors of automatic door, control system of door and gate, car key remote, auto parts etc. The company currently has four independent brands: U-CONTROL, U-SENSORS, U-AUTOGATES and U-AUTOKEYS.
-
got questions? call us
+86 13960286508
-
fax :
+86 595 22901208 -
Email :
[email protected]
-
address
- No.991 Xingxiu Road,Taiwanese Investment Zone, Quanzhou, Fujian Province,P.R.China