In modern homes, garage door remote controls have become indispensable, providing convenience and security. One of the most critical factors for users is the effective operating range of the remote control. Different models of remote controls can vary significantly in range, from 10 meters to 100 meters, directly affecting the user experience. Ideally, users want to be able to operate the garage door from a considerable distance, even from outside the garage or far from the door itself. This not only enhances convenience but also increases the user’s sense of security. This article will explore the factors influencing the operating range of garage door remote controls, analyze the impact of different technologies on this range, and discuss how to optimize remote control design and usage environments to meet the user demand for stable operation at a distance.
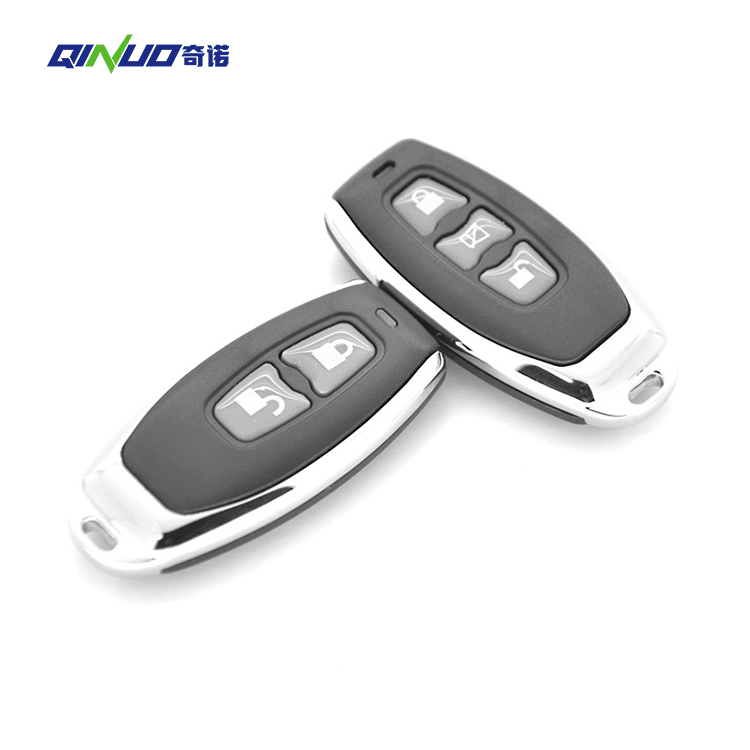

1. Basic Concepts of Remote Control Operating Range
1.1 Definition of Remote Control Operating Range
The remote control operating range refers to the maximum distance within which the remote control can effectively transmit signals and control the opening and closing of the garage door. Within this range, the signal from the remote control can be reliably received and decoded by the garage door receiver, enabling the desired door operation. This range is a crucial performance indicator of the remote control, influencing the convenience and overall experience of the user.
1.2 Major Factors Affecting Remote Control Operating Range
The effective operating range of a remote control is influenced by several factors, including:
Signal Frequency: Remote controls typically use radio waves for signal transmission, with different frequencies having varying propagation characteristics. Lower frequency signals tend to have better penetration but shorter ranges, while higher frequency signals can travel farther but are more susceptible to interference from obstacles.
Transmission Power: The higher the transmission power of the remote control, the farther the signal can typically travel. However, increased transmission power also results in higher power consumption, necessitating a balance between power and battery life.
Receiver Sensitivity: The sensitivity of the garage door receiver determines how weak a signal it can pick up. Higher sensitivity allows the receiver to capture signals over a broader range.
Environmental Factors: Signal propagation is also affected by the surrounding environment. Obstacles such as buildings, walls, metal objects, and trees can weaken or reflect signals, reducing the effective operating range of the remote control.
Signal Interference: Other wireless devices operating on the same frequency band or electromagnetic interference (such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other remote controls) can also disrupt the remote control signal, leading to a shorter range or unstable operation.
2. Analysis of Signal Range in Different Remote Control Models
2.1 Short-Range Remote Controls (10-30 meters)
Short-range remote controls are typically designed for smaller garages or scenarios where the user operates the door from close proximity. These remote controls have lower transmission power and operate on lower frequencies, making them suitable for environments where signal transmission requirements are not stringent. The advantage of short-range remote controls is their low power consumption, which results in longer battery life. However, the drawback is that users must be close to the garage door for effective operation, limiting their usability.
2.2 Mid-Range Remote Controls (30-60 meters)
Mid-range remote controls are common in most residential garages, offering a moderate signal range that meets the needs for some distance operation without significantly increasing power consumption. These remote controls typically use medium-frequency signals that can penetrate common building materials, making them suitable for use in typical residential areas.
2.3 Long-Range Remote Controls (60-100 meters)
Long-range remote controls are designed to meet the needs of users who wish to operate the garage door from a considerable distance. These remote controls have higher transmission power and operate on higher frequency signals, allowing them to function reliably over longer distances. However, due to the higher power output, long-range remote controls consume batteries more quickly and may require more frequent replacements. Additionally, in complex environments, these remotes may encounter more signal interference.
3. Technical Methods to Extend Remote Control Operating Range
3.1 Increasing Transmission Power
One of the most direct ways to extend the operating range of a remote control is by increasing its transmission power. However, any increase in transmission power must comply with regulatory limits to avoid interfering with other wireless devices. Moreover, higher power output leads to higher power consumption, so a balance must be struck between range and battery life during the design phase.
3.2 Using High-Gain Antennas
The design of the antenna in both the remote control and receiver significantly impacts the operating range. High-gain antennas can transmit and receive signals more effectively, thus increasing the remote control's effective operating range. By optimizing the directionality and gain of the antenna, signal loss can be minimized, enhancing coverage.
3.3 Choosing the Appropriate Signal Frequency
The choice of signal frequency has a considerable impact on the remote control’s operating range. Generally, lower-frequency signals (e.g., 315 MHz, 433 MHz) offer better penetration and are suitable for environments with obstacles, while higher-frequency signals (e.g., 2.4 GHz) can travel longer distances but are more susceptible to obstacles and interference. Selecting the appropriate frequency based on the environment can improve the remote control’s effective range.
3.4 Enhancing Receiver Sensitivity
The sensitivity of the receiver determines how weak a signal it can detect. By improving receiver sensitivity, the operating range of the remote control can be extended. Incorporating low-noise amplifiers and high-performance filters into the receiver design can effectively enhance sensitivity, thereby boosting the overall system performance.
3.5 Reducing Signal Interference
Minimizing environmental signal interference is also crucial for extending the operating range of the remote control. This can be achieved by selecting a more isolated frequency band, employing frequency-hopping technology, or encrypting signal transmissions to reduce interference from other wireless devices. Additionally, installing the receiver away from sources of electromagnetic interference (such as Wi-Fi routers and high-power electrical appliances) can further enhance the remote control's stability and range.
4. Operating Range Requirements in Practical Applications
4.1 Residential Usage Requirements
In residential areas, users typically want to operate the garage door from the driveway entrance or from outside the home, avoiding the need to approach the garage door for operation. This usually requires a remote control operating range of 30-60 meters, capable of penetrating exterior walls or other obstacles. Therefore, mid-range remote controls are the best choice for residential areas, with attention to minimizing interference from nearby wireless devices.
4.2 Commercial Applications
In commercial settings or large parking lots, users may need to operate the garage door from a greater distance, especially when driving into the parking area. These scenarios usually require long-range remote controls with a signal range of 60-100 meters or more. Additionally, since commercial environments may have more wireless devices, interference resistance is a crucial consideration.
4.3 Special Environmental Requirements
In certain special environments, such as industrial zones or areas with numerous metal obstacles, the remote control signal may be heavily interfered with. In such cases, specialized high-frequency remote controls or the use of repeaters to boost signal transmission may be necessary. Additionally, special shielding measures for both the remote control and receiver may be required to reduce the impact of electromagnetic interference on the operating range.
5. Design Suggestions for Optimizing User Experience
5.1 Providing Adjustable Operating Range Options
To meet the diverse needs of users, remote controls could be designed with adjustable operating range options. For example, by allowing users to adjust the transmission power or switch between different signal frequencies, they can select the most suitable operating mode based on their actual environment. This not only enhances the versatility of the remote control but also optimizes its performance in different environments.
5.2 Adding Feedback Features
To give users a better sense of control over the operating range, feedback features such as LED indicators or buzzers could be added to the remote control. When the remote control successfully sends a signal and is recognized by the receiver, the feedback device can alert the user, confirming that the operation was successful. This design helps reduce uncertainty, particularly when operating from a distance.
5.3 Considering Energy Efficiency and Battery Life
Battery life is a critical factor in the user experience with remote controls. While increasing transmission power can extend the operating range, it also accelerates battery consumption. Therefore, it is essential to strike a balance between operating range and battery life during remote control design, or to adopt efficient energy management technologies, such as low-power modes and intelligent wake-up features, to extend battery life.
5.4 Utilizing Environmental Adaptation Technology
Remote controls can incorporate environmental adaptation technology that automatically detects the surrounding signal strength and interference levels, adjusting transmission power and signal frequency accordingly. This technology optimizes the remote control's performance in complex environments, ensuring stable operation in various scenarios.
6. Future Development Trends
6.1 Adoption of Advanced Wireless Communication Technologies
As wireless communication technologies continue to advance, future garage door remote controls may adopt more sophisticated technologies, such as 5G communication or Internet of Things (IoT) technology. These technologies can not only provide longer operating ranges but also enable more complex control functions and greater interference resistance, offering users a more intelligent and convenient experience.
6.2 Wireless Charging and Long Battery Life Design
Future remote controls may adopt wireless charging technology, eliminating battery life concerns altogether. Users could place the remote control on a wireless charging pad inside the car, ensuring it is always fully charged. Additionally, the use of more efficient power management chips and energy recovery technologies could further extend the battery life, even with frequent use.
6.3 Smart Connectivity and Remote Control
With the rise of smart homes, future garage door remote controls may connect to smartphones or other devices, enabling remote operation and status monitoring. Users could control the garage door remotely via a mobile app or set up automatic operation modes, further enhancing convenience and security.
Conclusion
The operating range of a garage door remote control is a critical factor affecting user experience. Different usage environments and needs require diverse design considerations for remote controls. By optimizing transmission power, selecting the appropriate signal frequency, enhancing receiver sensitivity, and reducing environmental interference, the operating range and stability of remote controls can be significantly improved. In the future, as wireless communication technology and smart home technology continue to develop, garage door remote controls will become more intelligent and efficient, offering users a safer and more convenient experience. In designing and using remote controls, it is essential to consider user needs, environmental factors, and technological trends comprehensively to create high-quality products that meet market demands.

-
Office ViewQinuo Electronics Co., Ltd.was founded in 2009,it is a high-tech company that integrated R & D, manufacturing, sales and service for 15 years,which is mainly specialized in providing sensors of automatic door, control system of door and gate, car key remote, auto parts etc. The company currently has four independent brands: U-CONTROL, U-SENSORS, U-AUTOGATES and U-AUTOKEYS.
-
got questions? call us
+86 13960286508
-
fax :
+86 595 22901208 -
Email :
[email protected]
-
address
- No.991 Xingxiu Road,Taiwanese Investment Zone, Quanzhou, Fujian Province,P.R.China